Cloud service providers (CSPs) and their customers share the responsibility for securing the client’s cloud infrastructure and data resources. Both entities play a vital role in protecting the cloud environment from threat actors. Companies need to fully understand the details of the cybersecurity measures implemented by the CSP so they can play their part in securing their valuable cloud environment. Organizations that do not understand and fulfill their responsibilities in securing their cloud infrastructure risk damaging their business..
What is the Shared Security Responsibility Model?
The shared security responsibility model defines the specific responsibilities of a CSP and their customers in securing their cloud environment. The CSP is generally responsible for the security of the cloud, with the customer assuming responsibility for securing the data and resources in the cloud.
Every CSP should have documentation available for customers that outlines each party’s role in protecting cloud resources. The models from various CSPs are generally very similar, but there may be differences in the description or responsibility for specific tasks. Companies should consult their CSP’s model to verify their role in protecting the cloud environment.
We are going to use the AWS shared responsibility model for this discussion. Let’s look at how AWS defines the shared responsibilities. AWS provides the following chart to differentiate CSP and client security responsibilities.
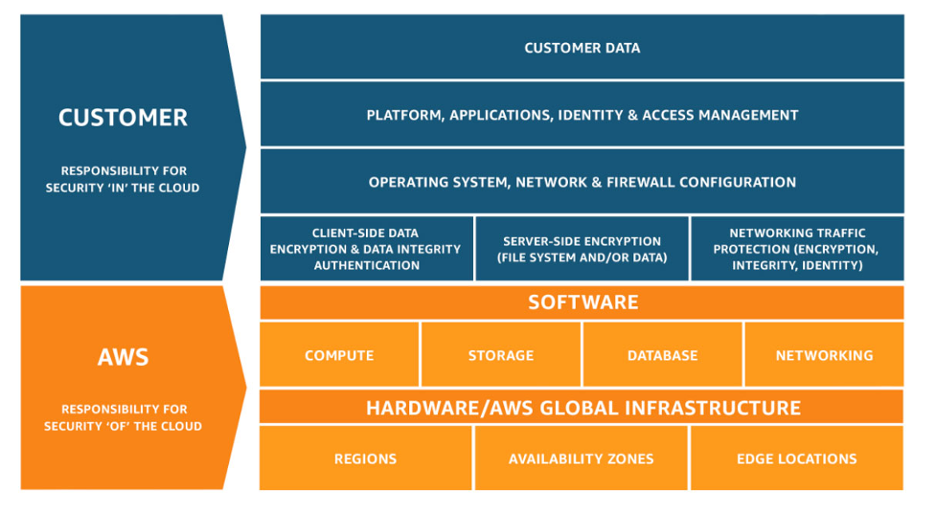
CSP responsibilities
AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud. The CSP is in charge of protecting the infrastructure components that run all AWS cloud services. The infrastructure includes all the hardware, software, networking, and facilities used to provide AWS cloud services to customers. The CSP secures the physical servers and networks from security risks. They are also responsible for managing and securing the virtualization layer that lets customers create virtual machines and responding to security incidents that may affect the operation of physical cloud infrastructure components.
The chart indicates that AWS secures the underlying cloud infrastructure’s compute, storage, database, and networking software. The CSP is also responsible for securing the various regions and availability zones and protecting access to cloud services from a customer’s edge locations.
Customer responsibilities
The customer is responsible for aspects of cloud security, which can vary based on the specific AWS services the client selects. We will discuss these differences in depth in the next section of this article. The primary customer responsibility is to protect the company’s data resources stored and processed in the cloud. Customers must implement and manage client data encryption and identity and access controls to protect information from unauthorized access or breaches.
Securing customer data is always the customer’s responsibility and must be prioritized by organizations with a cloud environment. Customers may additionally be responsible for securing platforms and applications. Depending on how they utilize cloud services, the customer may be charged with making operating system, network, and firewall configurations.
How the Shared Model Applies to Different Cloud Delivery Models
An organization’s shared security responsibilities vary based on the cloud delivery model or models used to construct its infrastructure. Companies with multiple cloud environments may be utilizing more than one model. Teams must understand how the model type affects their responsibility to protect it. In some cases, it can be challenging to determine which party is responsible for security.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
The CSP only provides the infrastructure in the IaaS cloud delivery model. The CSP is responsible for securing the physical infrastructure and virtualization layer. Customers manage security for all other aspects of the environment. Security responsibilities are clearly defined in the IaaS model due to the clear distinction between the cloud infrastructure and customer workloads. Customers have the highest degree of security responsibility in the IaaS model.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
A CSP provides customers with the infrastructure and tools to develop and deploy systems and applications. The CSP manages and secures the infrastructure, software development, and deployment tools. Customers manage and secure the systems and applications they create and deploy. Responsibilities include implementing and enforcing encryption and identity and access management (IAM) to eliminate unauthorized use of the applications on the platform. Customers must understand the CSP’s security measures and address all other platform security requirements.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
The CSP provides applications and solutions for customer use in the SaaS model. The CSP secures virtually all aspects of an SaaS application except customer data. Customers are responsible for protecting their data with encryption and access controls. Organizations should also implement backup procedures to guard against data loss or corruption.
Why it is Essential to Understand the Shared Responsibility Model
Companies must understand the shared responsibility model for several reasons.
- Accountability – Customers need to understand their role in protecting cloud resources. While the customer is always accountable for protecting its data, security for systems, platforms, and applications varies. Companies should verify the CSP’s security measures and never assume that specific safeguards are in place.
- Incident response – Organizations must know which party will respond to security incidents. A misunderstanding can result in delayed action to address a cyberattack or data breach that can exacerbate business damage.
- Risk mitigation – Customers who misunderstand the details of the model may expose themselves to security gaps and vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory compliance – CSPs provide companies processing regulated data with compliant infrastructures to meet the requirements of standards such as GDPR or HIPAA. However, the customer is responsible for compliance, such as ensuring the data is encrypted.
- Operational efficiency – Customers who understand the roles of both parties can avoid duplicating tasks handed by the CSP.
How VAST Can Help Secure Your Cloud Environment
VAST’s strategic partnerships and expertise with the major cloud providers’ platforms put us in a great position to help your business secure its cloud environment. Our security lifecycle review enables you to uncover vulnerabilities and develop a strategy to secure your cloud resources. We support the Bitglass cloud access security broker (CASB) to strengthen your cloud security and ensure your data is safe.
Talk to our security experts and let us help you navigate the potential complexities of the cloud shared security responsibility model.



